With a new focus on both continuous innovation and new product development, the world of opportunity for developers and DevOps specialists has abruptly transformed. With an eye toward the future, we’ve selected some of the things.
What Are DEVOPS and How Do They Work in the Current Trend?
- A company’s ability to deliver applications and services at high velocity is enhanced by the DevOps combination of cultural philosophies, practices, and tools.
- As a result, products evolve and improve more quickly than they would in organizations using traditional software development and infrastructure management processes.
- IT currently plays a critical role in attaining business objectives in the great majority of enterprises.
Why Do DEVOPS Operate?
- As we mentioned, the DevOps ecosystem fosters collaboration between the development team and operations throughout the whole software lifecycle, leading to the development of a broad range of capabilities.
- When security is the primary concern, a practice known as Dev Sec Ops is used. Security and QA teams may collaborate closely with DevOps.
- They employ procedures to automate -intensive manual processes.
The SDLC life cycle is divided into the following stages by the DevOps Lifecycle:
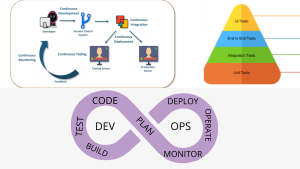
1. Continuous Development: During this stage, the code is committed to version control tools like Git or SVN for tracking the various versions of the code and to Ant, Maven, and Gradle for building/packaging the code into an executable file that can be sent to the QAs for testing.
2.Continuous Integration: This stage is crucial to the DevOps Lifecycle as a whole. Since it deals with merging the many DevOps lifecycle stages, it is essential to automating the entire DevOps Process.
3. Continuous Deployment: The code is built, the environment or application is containerized, and the server of choice is deployed at this point. Configuration management, virtualization, and containerization are the crucial procedures in this phase.
4. Continuous Testing: This stage deals with testing the program that the developer has pushed through an automated process. When there is a problem, the notification is delivered back to the integration tool, which then alerts the developer. The message is forwarded to Integration-tool, which sends the build to the production server if the test was successful.
5. Continuous Monitoring: The stage keeps an eye out for errors or failures in the deployed application. It can be configured to gather user input. The data is subsequently forwarded to the programmers so they can enhance the application.
What Groups Use DevOps and Why?
- DevOps is being embraced by IT firms all across the world, from large corporations to early-stage startups. The following are a few businesses that have adopted DevOps:
- Internet-based companies like Amazon, Facebook, Netflix, etc.
- Media firms like Sony Pictures provide financial services.
- manufacturer of construction goods like USG
- Small and medium-sized firms, such as The US Patent & Trade Office, are governed by governments and semi-governments.
- In addition to businesses, DevOps is an excellent strategy for people like: developers and programmers free from the annoyances of protracted paperwork, approval processes, and server requirements.
- In this manner, developers may quickly set up the ideal working conditions and tools to be more inventive and creative. operational personnel with the capacity to collaborate closely with developers and increase the stability of software installations
- DevOps provides product managers, marketing directors, and business managers with quicker consumer input, better system responsiveness, decreased risks, and waste reduction.
- Executives can devote time to creating corporate expansion goals by not having to participate in every interdepartmental issue. DevOps culture also draws brilliant programmers, testers, system administrators, and other professionals because of the future scope.
How DEVOPS Influence the Future?
- Although organizational tactics and tooling are likely to alter in the future for DevOps, its primary goal will remain the same.
1.A Major Role for Automation:
- AI Ops, or artificial intelligence for IT operations, will assist businesses in achieving their DevOps objectives while automation will continue to play a significant role in the DevOps transition.
2.Routine operational procedures can be expedited by combining the major components of AI Ops:
- Machine learning, performance baselines, anomaly detection, automated root cause analysis (RCA), and predictive insights.
- In the future of DevOps, this cutting-edge technology—which has the potential to revolutionize how IT operations teams handle warnings and address problems—will be a key element.
3.Will Increase Attention to Cloud Optimization:
- The optimal utilization of cloud technology will receive more attention in the future of DevOps. According to Deloitte Consulting analyst David Linthicum, the centralized aspect of the cloud gives DevOps automation a common platform for testing, deployment, and production.
- In addition, enterprises will need to understand that DevOps is all about the journey and that the organization’s DevOps-related goals and expectations will change over time, regardless of what cutting-edge technologies the future offers.
Future difficulties for DevOps:
- A DevOps faces numerous difficulties. To make operations more efficient, your company must rethink its organizational structure. However, businesses sometimes underestimate how much worker goes into a DevOps shift. A recent Gartner analysis found that problems with organizational learning and change will prevent 75% of DevOps program from succeeding by 2020.
- “For DevOps to succeed, organizational learning and transformation are essential. In other words, human factors—not technological factors—often provide the biggest problems, according to George Spafford, a senior analyst at Gartner.
It’s Difficult to Pick the Right Metrics:
- According to Forrester, businesses implementing DevOps principles must use metrics to track their progress, record their successes, and identify areas for improvement. An increase in deployment velocity, for instance, is not a success if there isn’t a corresponding improvement in quality. However, firms frequently struggle with DevOps KPIs, which are essential for an efficient DevOps operation. Some of the measures are:
- Little Money
- Other challenges confront DevOps attempts as well. Adjustments will take time due to the considerable organizational and IT changes required, including the uniting of formerly isolated teams, job role changes, and other transitions.
1.Complexity:
- Efforts in DevOps can get bogged down in complexity. Key executives may find it challenging to understand the business value of an IT leader’s efforts.
2. Negative metrics and unattainable objectives can be disastrous:
- DevOps initiatives can fail for a variety of reasons, including implementing a half-baked DevOps effort that embraces agile methodologies while keeping IT ops and engineering/development teams in traditional ways, or setting unrealistic expectations, tracking metrics that don’t align with business goals.
Conclusion:
- DevOps has a huge impact on business operations. By bridging the chasm between developers’ demand for change and operations’ opposition to change, it creates a smooth road for Continuous Development and Continuous Integration. Think about performing a DevOps self-analysis as well.
- Maximizing the value transfer from the concept to the end user is DevOps’ primary goal. Culture is obviously a big consideration because a company must experience a cultural transition in order to be successful with DevOps, but the goal of DevOps is to improve the efficacy and efficiency of value delivery.
- Implementing DevOps increases employee engagement by streamlining procedures and removing roadblocks inside your organization, allowing people to perform better work and feel more connected to one another.
